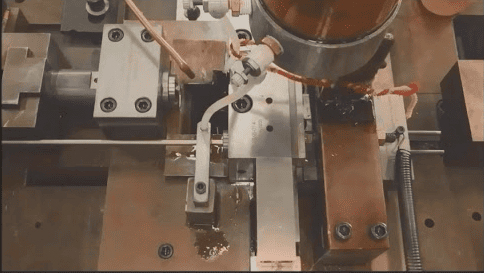
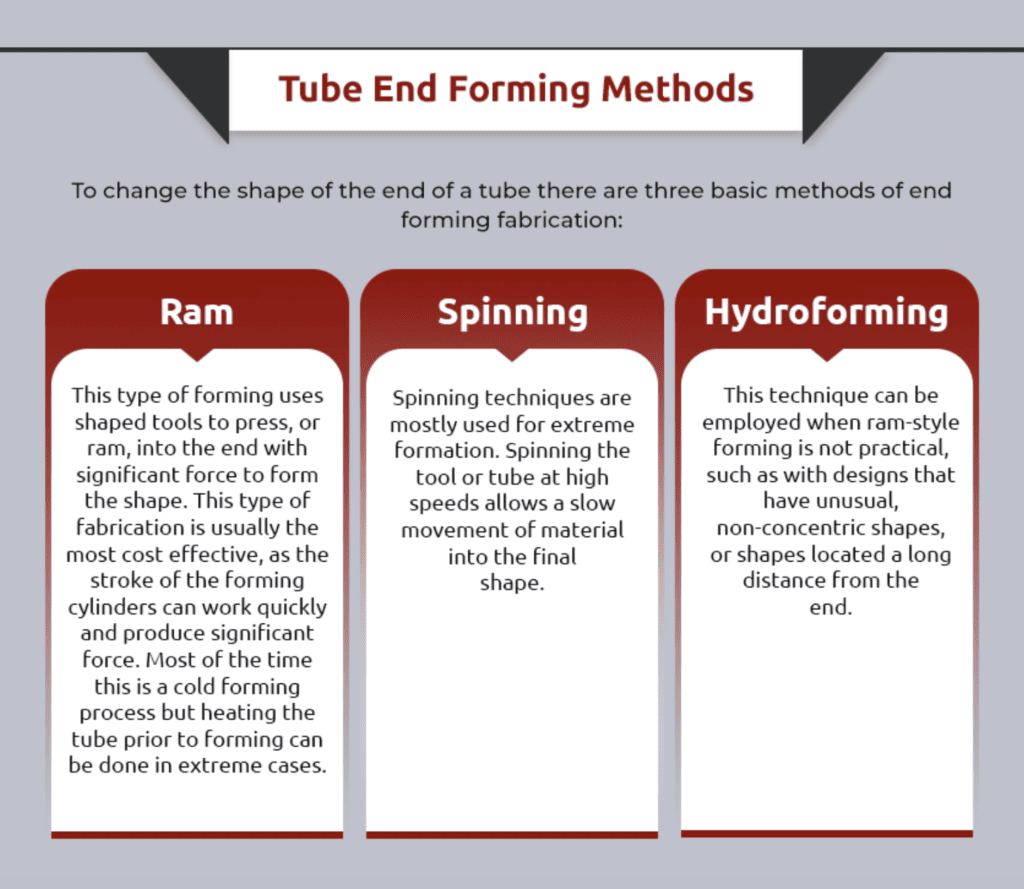
G & J Steel & Tubing, Inc. uses two different methods of end forming (Shear-Form® and Ram) to suit a wide variety of applications. Our proprietary Shear-Form® process is a unique, single-operation cutoff and end-forming process for high speed capability on small diameter parts. We can work with all metals including aluminum, brass, copper, nickel and stainless steel.
Any end form shape is available, including bead, flange, flare, notch and swage. A partial list of end form shapes is published below, but we can form material into virtually any shape. Our end-formed tube parts are widely used as fuel injectors, exhaust systems, discharge tubes, steering column parts, conduit, fluid transfer tubes, and gas filter stems, among many others.